The solar proposal is a response to Arizona electric utility Salt River Project’s request for proposals to site and supply a total of 400 MW of solar power. NTEC is partnering with Photosol, a world leader in renewable energy storage solutions, with decades of expertise in solar development. Photosol currently has over 382 MW of solar plants in operation and construction along with an over 7,500 MW project pipeline. The solar proposal builds upon NTEC’s commitment to conscientious energy development.
From Navajo Transitional Energy Company:
June 18, 2020
Navajo Transitional Energy Company (NTEC) is pleased to announce that the company has partnered with Photosol US (Photosol) establishing the next step toward building a renewable energy portfolio on the Navajo Nation. Today, the companies submitted a proposal to site 200 MW, of a 400 MW, solar array on reclaimed Navajo Mine land.
If accepted, the project could generate up to $20 million in tax revenues for the Navajo Nation over 40 years. “Including solar and other renewable energy sources in NTEC’s portfolio has always been part of our vision for NTEC and the Nation,” said Chairman Timothy McLaughlin. “We are excited for the opportunity to transition the reclaimed land at Navajo Mine to the production of renewable energy that has the potential to provide long-term revenues for the Nation.”
The solar proposal is a response to Arizona electric utility Salt River Project’s request for proposals to site and supply a total of 400 MW of solar power. NTEC is partnering with Photosol, a world leader in renewable energy storage solutions, with decades of expertise in solar development. Photosol currently has over 382 MW of solar plants in operation and construction along with an over 7,500 MW project pipeline. The solar proposal builds upon NTEC’s commitment to conscientious energy development.
Last year the company invested in Texas Mineral Resources, a company which is developing innovative extraction methods for rare earth minerals and metals, that are key component of solar panels and the batteries necessary to store solar energy and power electric vehicles. McLaughlin said, “It is very exciting to play a role in developing two of the key components to a viable solar powered future—the minerals and metals necessary for the infrastructure and the solar array that will generate the power on Navajo land.”

 Sheriff's Office Investigates Fatal Shooting
Sheriff's Office Investigates Fatal Shooting
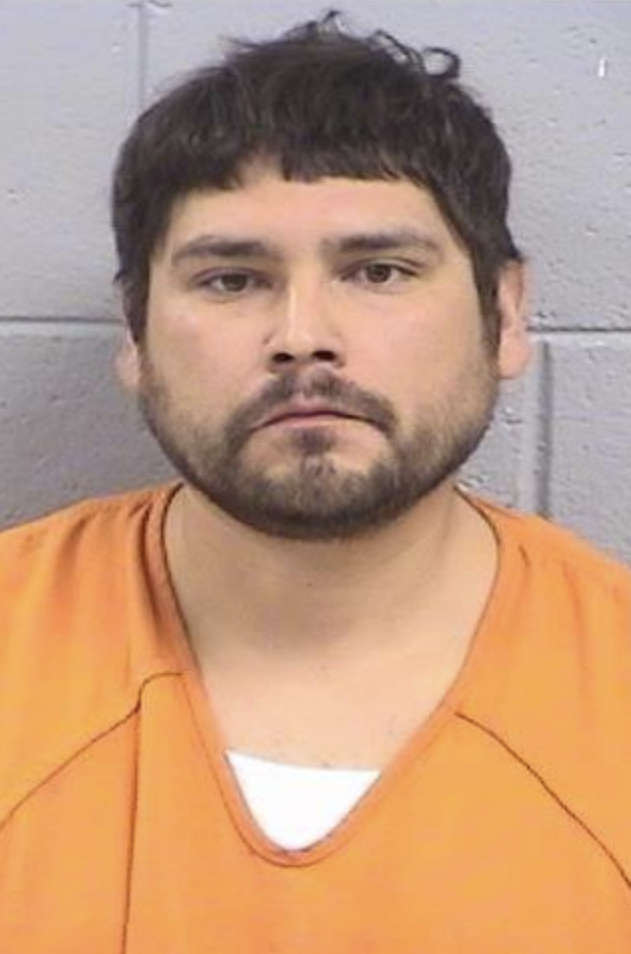 Suspect Arrested in Farmington Murder Case
Suspect Arrested in Farmington Murder Case
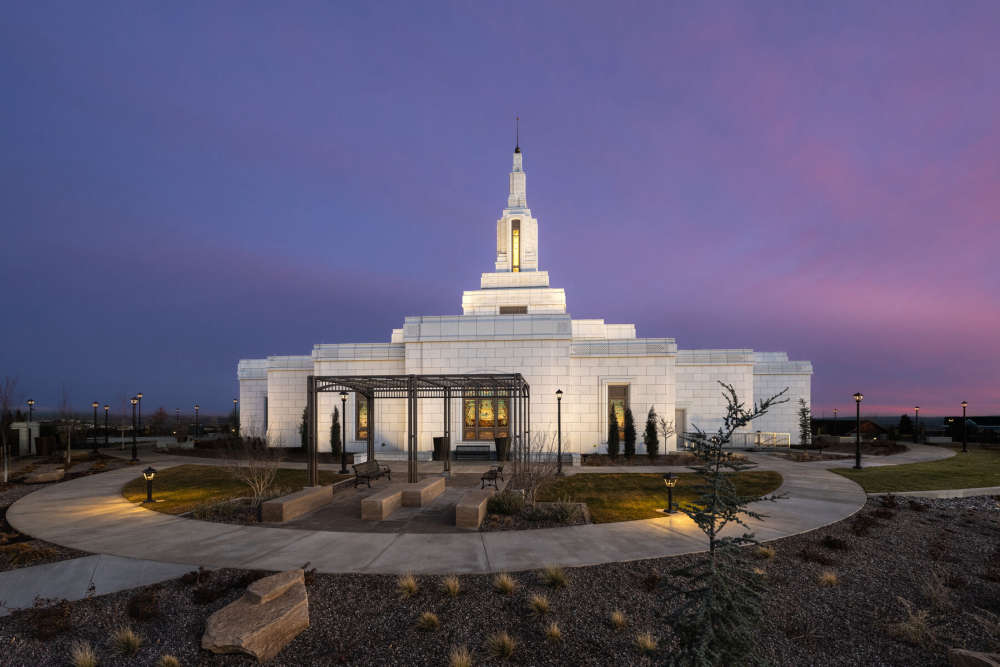 Farmington Temple Opens this Summer
Farmington Temple Opens this Summer
 Police: Farmington Child Abuse Suspect Killed in Home
Police: Farmington Child Abuse Suspect Killed in Home
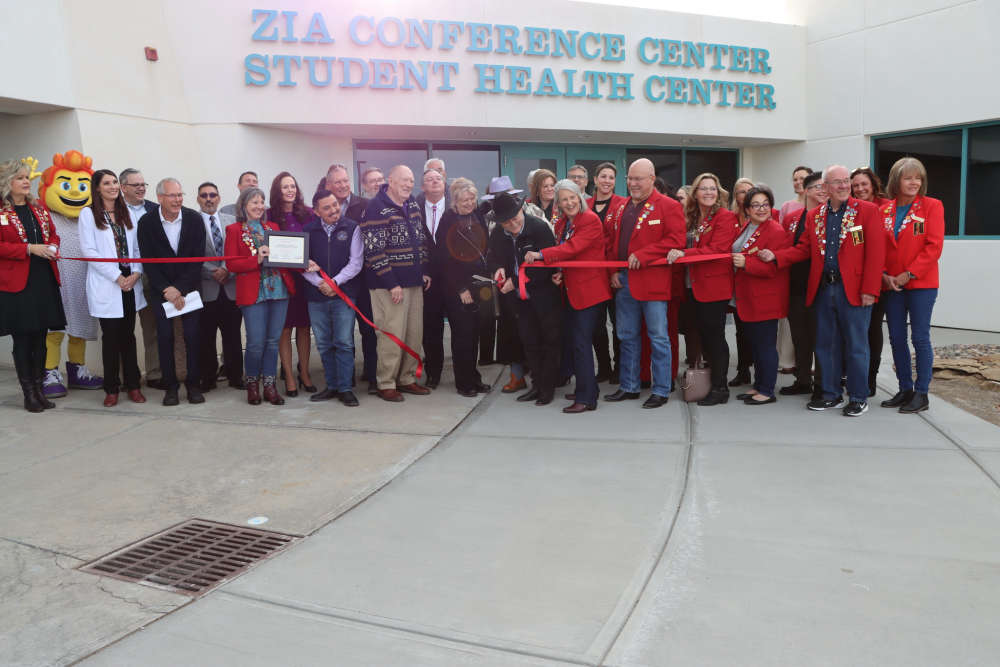 College Opens new Student Health Center
College Opens new Student Health Center
 Farmington Couple Accused of Severe Child Abuse
Farmington Couple Accused of Severe Child Abuse